This post is dedicated to studying the co-ordinate covalent. This is a bond formed between an electron-rich and an electron-poor species.
Electron rich species → Lewis base → electron donor
Electron deficient/poor species → Lewis acid → electron acceptor

If a rich man and a poor guy become friends, the rich man will lend his extra money to the poor man and they will bond well. Similarly, when an electron-rich species(Lewis base) donates its electrons to an electron-deficient species(Lewis acid), a coordinate covalent bond is formed between them. In this type of bond, only one atom provides both the shared electrons. The other atom just accepts those electrons. This is different from a covalent bond where electrons are shared by both atoms.
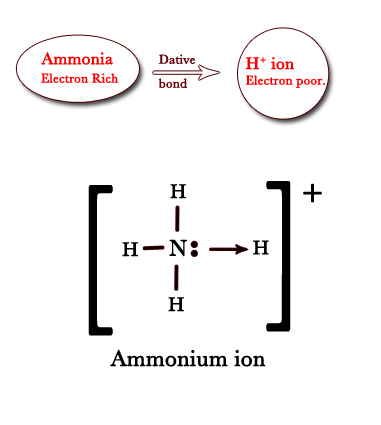
e.g. – i)Ammonium ion (NH4+) – In this ion, the nitrogen in the ammonia molecule has a lone pair of electrons. Thus, ammonia is electron-rich. The hydrogen ion (H+) is formed when hydrogen loses the 1s electron. Thus, the hydrogen ion is electron deficient. Ammonia lends its lone pair to hydrogen ions to form a coordinate bond between the two. Note that in this bond the electrons shared between two species come from ammonia only.
ii) Ammonia diborane – Just as above, ammonia can end its lone pair to borane molecule, which is electron deficient as follows –
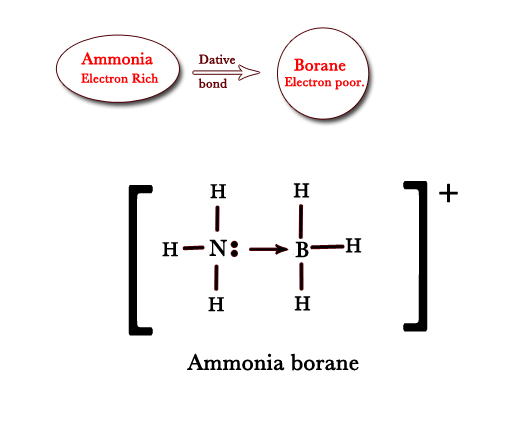
A co-ordinate bond is shown by the ‘→’ sign. The arrow is drawn from the electron donor to the electron acceptor. However, this bond is shown just as a single line with a positive(+) sign on the donor and a negative sign(-) on the acceptor atom.
The co-ordinate bond forms the basis of a whole class of compounds called coordination compounds. In these compounds the transition metals, which have vacant d- orbitals act as electron acceptors(Lewis acids), and the electron donors are called ligands (Lewis bases). We will study coordination chemistry in detail in some later posts. Here is an example of such metal complex –

The central cobalt ion is accepting electrons from 4 ammonia and two chlorine ligands. All those bonds are co-ordinated bonds and thus this is a coordination compound.
The electron-rich species are negatively charged ions or neutral molecules with lone pair/s.
These have melting and boiling points higher than the covalent compounds but lower than the ionic compounds. This means that co-ordinate covalently bonded compounds are more stable than the covalent compounds. However, the ionic bond is the strongest.
In the next post, we shall start discussing secondary bonding in molecules. Till then,
Be a perpetual student of life and keep learning…
Good day!
Image source –
1.https://www.123rf.com/stock-photo/rich_poor.html?sti=lk7idadnv4soc49qcq|